
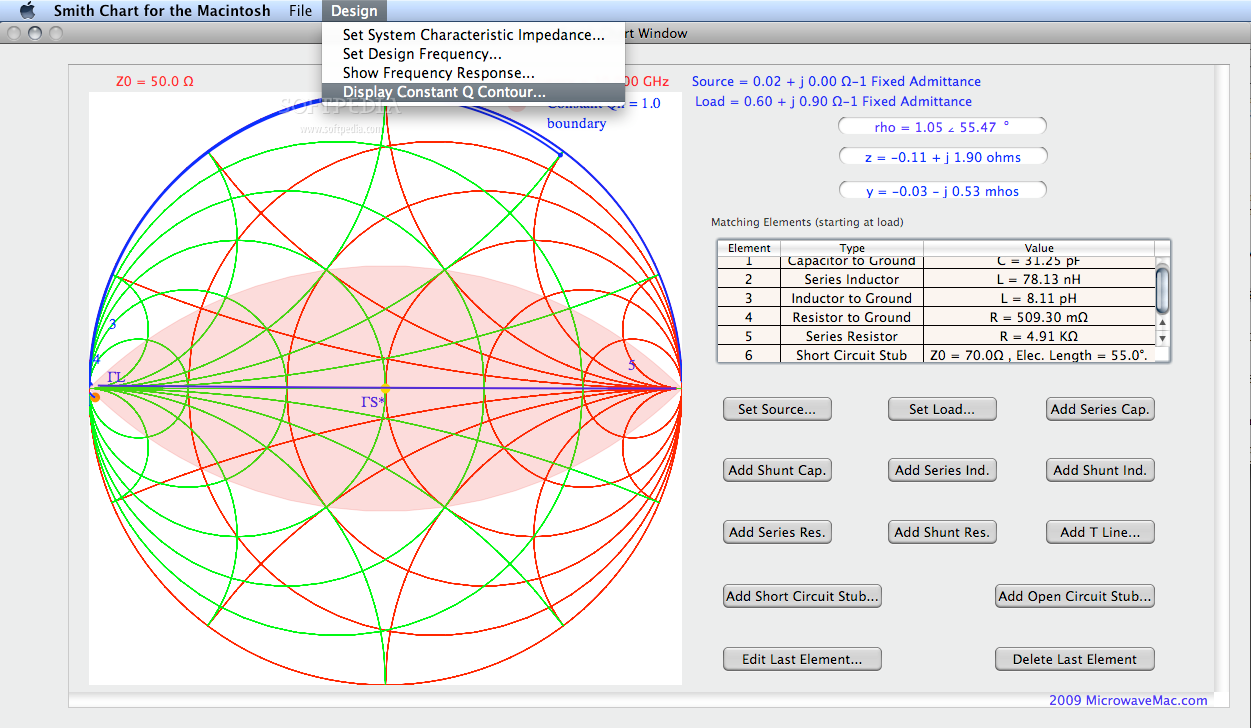
Knowing the values of n-1 variables, the value of the unknown variable can be found, or by fixing the values of some variables, the relationship between the unfixed ones can be studied.
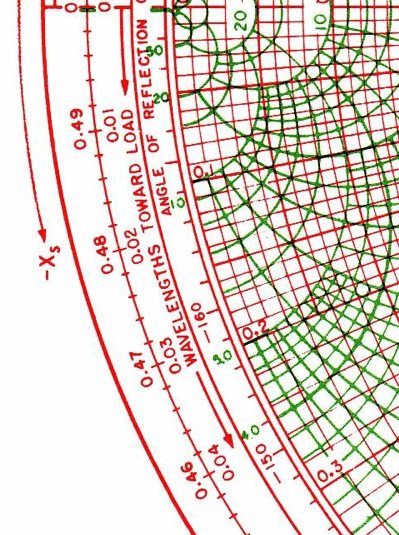
Nomograms use a parallel coordinate system invented by d'Ocagne rather than standard Cartesian coordinates.Ī nomogram consists of a set of n scales, one for each variable in an equation. The field of nomography was invented in 1884 by the French engineer Philbert Maurice d'Ocagne (1862–1938) and used extensively for many years to provide engineers with fast graphical calculations of complicated formulas to a practical precision. The isopleth crosses the scale for T at just under 4.65.Ī nomogram (from Greek nomos νόμος, "law" and grammē γραμμή, "line"), also called a nomograph, alignment chart, or abac, is a graphical calculating device, a two-dimensional diagram designed to allow the approximate graphical computation of a mathematical function.
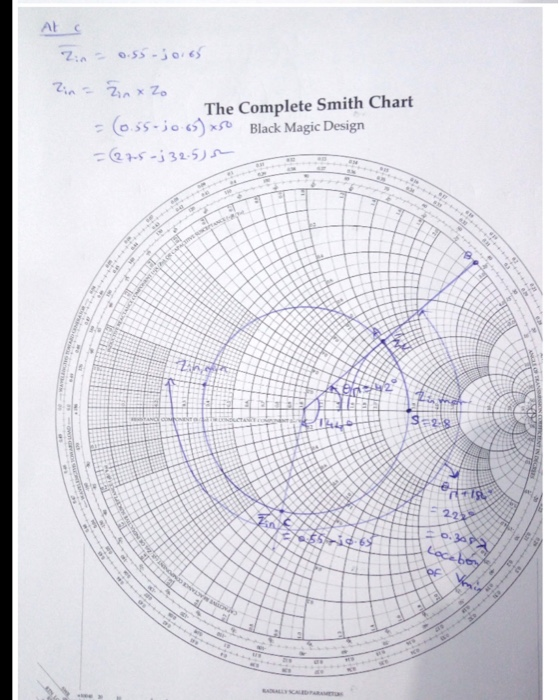
This example calculates the value of T when S = 7.30 and R = 1.17 are substituted into the equation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
